How to choose the correct gate type and the correct mold steel?
- Share
- Issue Time
- Jan 24,2018
Gate Type & Mold Steels
The type of gate depends upon a number of factors including the following:
1. Are you using hot runner or cold runner? Both runners have a number of gate types to choose from. For example, commonly used gates for cold runners are tab, submarine and pin gates. For hot runners hot tip and valve gates.
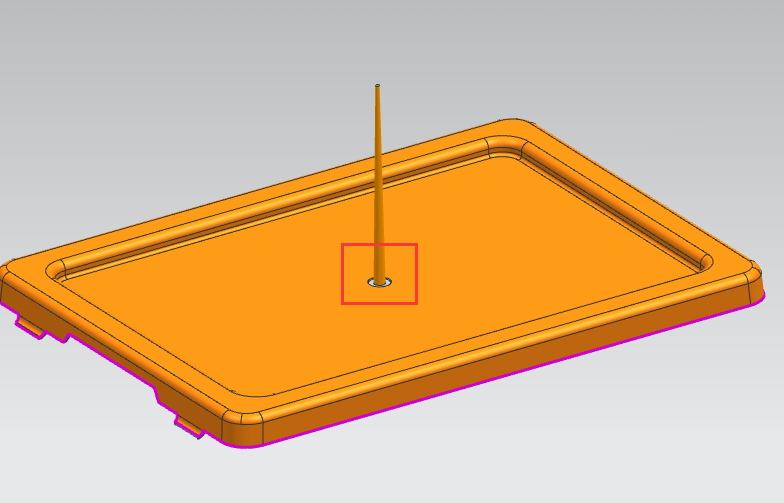
2. The shape of the part influences the type of gate. For example, flat parts often use a tab gate. Flat parts can also use valve gates for hot runners and allow gating in the centre of the part (such as a lid) and leave a clean flat gate mark.
3. Part material. Some plastic materials require a larger gate because they are shear sensitive (such as PET) than other materials so a large tab gate for a cold runner design or a valve gate for a hot runner design are often used. Pin gates or hot tip gates should be avoided with shear sensitive materials.
4. Part cosmetic requirements. Some gates are designed to leave minimal gate vestige such as a submarine gate.
Finally, the type of gate used is very dependent on the application. Every part has different requirements so each one must be studied on a case by case basis.
The plastic injection mold material mainly depends upon the annual shot quantity requirement. But it also depends upon part design and part plastic material.
For shot quantity requirements of less than 500,000 prehardened tool steel (called P20) is most commonly used for cores and cavities and the plastic injection mould base.
Although mild steel could also be used for the mould base as well.This steel is cheap.
Also, aluminium is growing in popularity in the automotive sector.Aluminium is much easier to machine and handle compared with tool steel so the cost of manufacture is less.Cycle times are also better but mold maintenance is critical to ensure part quality – anybuild up of residue will damage the shut off surface and cause part flashing.
Anything above 500,000 the use of thru hardened tool steels such as H13 or H11 should be considered for the cores and cavities. These materials will produce quality parts for much longer than P20 or aluminium because plastic injection mould wear is less.
For corrosive environments such as when molding PVC plastic, stainless steel tool steels can also be used in mold construction. Stainless steels will minimize corrosion.
On a more advanced level, cavity filling analysis is useful to predict the melt front advancement in the cavity and identify the location of knit-lines, end of fill, and other phenomena before the mold is manufactured and tested.